Suspenso in english
suspense
pronunciation: səspens part of speech: noun
pronunciation: səspens part of speech: noun
In gestures
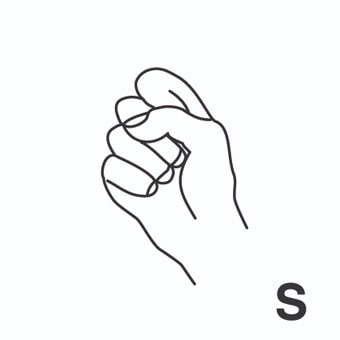
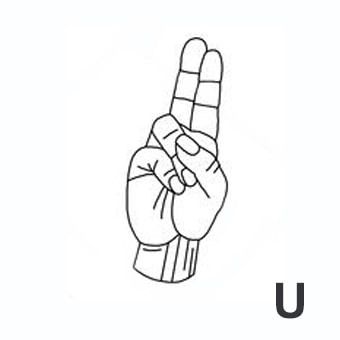

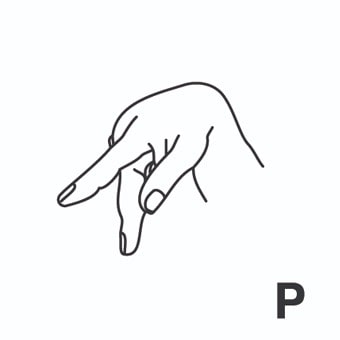
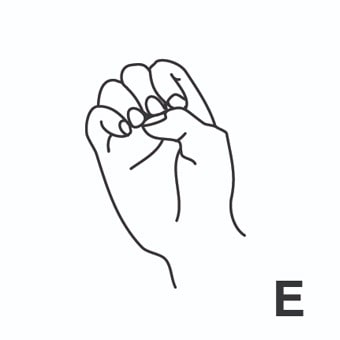


suspenso = flunked-out ; fail grade ; fail.
Example: The purpose of this study was to analyze the significant variables influencing the readmission of flunked-out students.Example: Students absent from exams will automatically get a fail grade.Example: Weekly quizzes are graded on a pass/fail basis, and they are worth 20% of your grade.more:
» dejar en suspenso = put + Nombre + into abeyance ; put + Nombre + on the back burner .
Example: He decided there would be other opportunities to broach the subject and so put it into abeyance. Example: She put her education on the back burner for several years so that her husband could get his first.» dejar una idea en suspenso = put + an idea on the back burner .
Example: My girlfriend and I looked at rings together about a year ago, then put the idea on the back burner because of money issues.» en suspenso = on the back burner [También se usa on a back burner] ; back burner .
Example: Although the prospect of compulsory competitive tendering in libraries is on the back burner it has put acquisitions firmly in the limelight. Example: Assistive technology will continue to be a back burner issue in most libraries.» mantener suspenso en el aire = suspend .
Example: Do not suspend a book by holding its casing only.» número de suspensos = failure rate .
Example: However, the failure rate in examinations at Sheffield does not seem to be at all high = No obstante, el número de suspensos en los exámenes de Sheffield no parece ser del todo alto.» porcentaje de suspensos = failure rate .
Example: However, the failure rate in examinations at Sheffield does not seem to be at all high = No obstante, el número de suspensos en los exámenes de Sheffield no parece ser del todo alto.» quedar en suspenso = go into + abeyance .
Example: The work, however, went into abeyance during the Second World War and its immediate aftermath.» tasa de suspensos = flunk-out rate .
Example: A dropout and flunk-out rate of 50% during the freshman year is occurring in many large municipal institutions of higher education.