Radiación in english
Radiation
pronunciation: reɪdieɪʃən part of speech: noun
pronunciation: reɪdieɪʃən part of speech: noun
In gestures
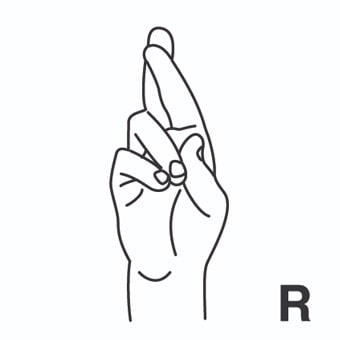
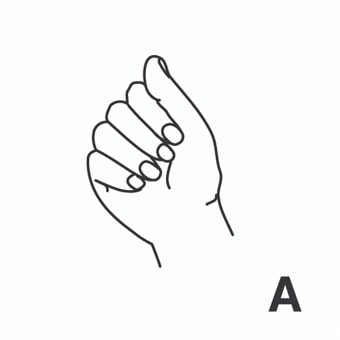
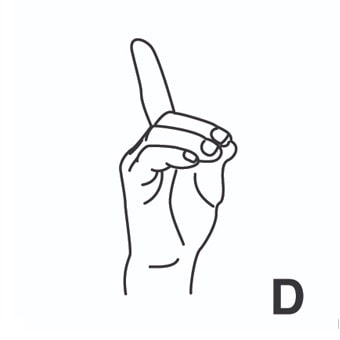


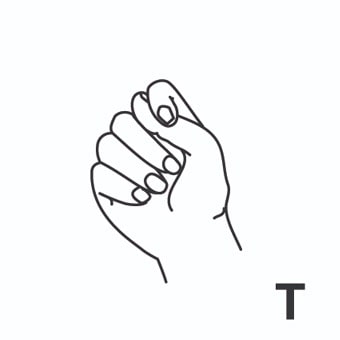

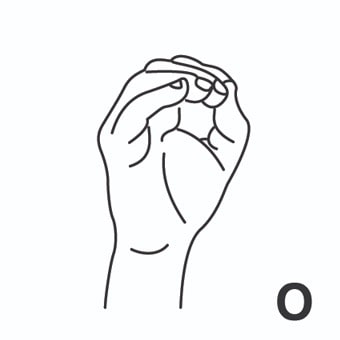
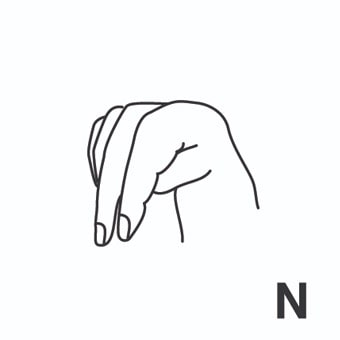
radiación = radiation ; irradiation.
Example: A radiograph is a photograph produced by the passage of radiation, such as X rays, gamma rays, or neutrons, through an opaque object.Example: The physical properties of gum arabic was not significantly altered by the electron beam irradiation.more:
» fuente de radiación = radiation source .
Example: Radio waves are utilized for transmission between aerials (antennas), or radiation sources and sensors.» química para la radiación = radiation chemistry .
Example: The author describes the design, structure, and use of numeric data bases for property data derived from photochemistry, photophysics, and radiation chemistry.» radiación electromagnética = electromagnetic radiation .
Example: There are those who argue the string of pylons will deface the landscape, and there are those who insist the electromagnetic radiation will give everyone cancer.» radiación ionizante = ionising radiation .
Example: Exposure to ionising radiation can increase the risk of cancer and high doses can cause serious damage, including radiation burns.» radiación nuclear = nuclear fallout ; fallout .
Example: Both films were treated with a gold-toning process to give increased protection from atmospheric pollution, including nuclear fallout. Example: The resulting cloud rose to a height of 12000 feet and subsequent fallout drifted in an easterly direction, travelling as far as 225 km from ground zero.» radiación solar = solar radiation ; solar gain .
Example: In this way the heat generated by the lighting, people and solar radiation is recovered to heat the building. Example: Large glazed areas mean that users can enjoy natural daylight, but double glazing, tinting, or architectural shading are necessary to alleviate the worst effects of noise, solar gain and solar glare = Las áreas acristaladas permiten que los usuarios puedan disfrutar de la luz natural, aunque el doble acristalamiento, los cristales ahumados, o las sombras arquitectónicas son necesarios para reducir los efectos negativos del ruido, la radiación solar y el resplandor del sol.