Indexing in spanish
pronunciation: indeksɑθioʊn part of speech: noun

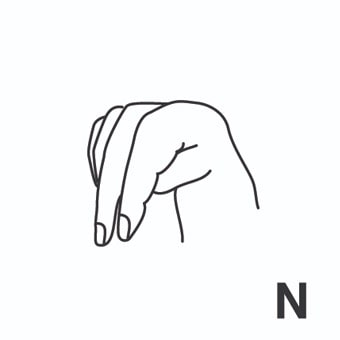
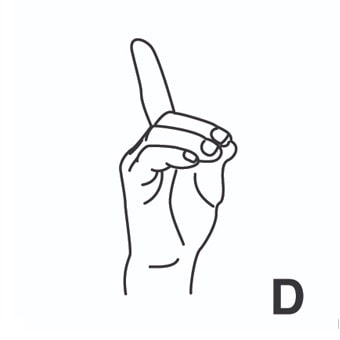
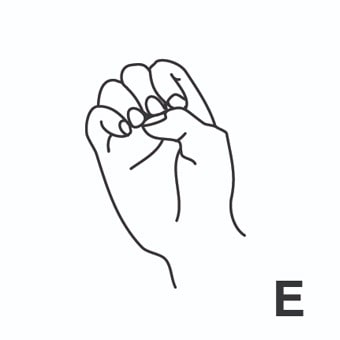
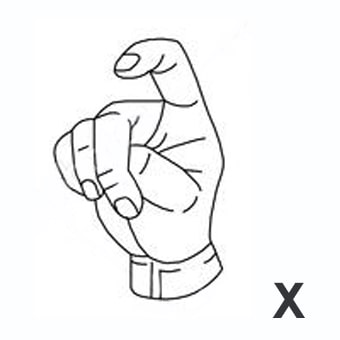
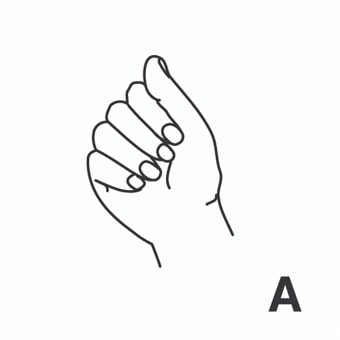
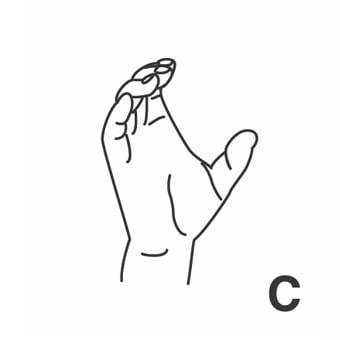

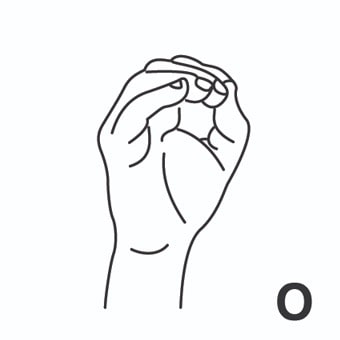

index3 = indizar. [Tercera persona singular indexes]
Example: For example a set of slides for use by teachers may be indexed according to alphabetical subject headings.more:
» chain index = indizar en cadena.
Example: In order to overcome some of the inherent weaknesses of the structure of DC it is important to chain index with reference to the essential relationships between subjects.» re-index [reindex] = volver a indizar.
Example: It was therefore decided to re-index the documents with a mean of 3.8 entries each.» thumb index = hacer un índice digital. [En un libro de referencia, muescas que se hacen en el borde externo para indicar las diferentes secciones del mismo; siendo este tipo de índice más comúnmente usado en diccionarios]
Example: The practising classifier is almost obliged to thumb index the volumes to make their use less time-consuming.indexing = indización. [Operación documental dirigida a representar por medio de un lenguaje documental o natural los datos resultantes del análisis del contenido de un documento]
Example: The features which contribute to UDC's suitability for detailed indexing are particularly valued in special libraries.more:
» abstracting and indexing journal = revista de resúmenes.
Example: There are several thousand abstracting and indexing journals available, and a large library may well take several hundred of these.» abstracting and indexing publication = publicación de resúmenes, revista de resúmenes. [Publicación secundaria de resúmenes]
Example: Title-based subject indexes have been used as indexes to local abstracting and indexing publications = Los índices de materias a partir de los títulos se han utilizado para indizar las publicaciones de resúmenes hechas por la propia biblioteca.» abstracting and indexing service = servicio de indización y resumen. [Publicación periódica que contiene resúmenes e índices de los documentos publicados sobre uno o varios temas de especialidad]
Example: The approach in this case is almost invariably by subject and the principal categories of bibliographic aid employed are abstracting and indexing services.» abstracting and indexing tool = instrumento para resumir e indizar.
Example: Prior to the 1970s UDC was frequently to be found in large card indexes in special libraries and sometimes to be encountered in abstracting and indexing tools.» alphabetical indexing = indización alfabética. [Tarea bibliográfica consistente en la extracción y ordenación alfabética de ciertos elementos contenidos en una colección de documentos, como palabras del título, nombres, materias, etc., seguidos de una referencia a los documentos que los contienen]
Example: This brief chapter merely serves to draw together some common problems in alphabetical indexing (which feature in a different way in classification schemes).» alphabetical indexing language = lenguaje de indización alfabética. [Conjunto de términos utilizados para describir el contenido de los documentos para su almacenamiento (indización) y recuperación; por ejemplo, una lista de encabezamientos de materia o un tesauro]
Example: Alphabetical indexing languages specialise in establishing specific labels for subjects, and providing direct access to individual subjects.» automatic indexing = indización automática. [Representación del contenido de un documento por selección automática de palabras o términos extraídos del texto, o por asignación automática de términos extraídos de un lenguaje documental]
Example: Automatic indexing consist in the representation of the content of a document by automated selection of words or terms from its text or by automatic assignment of terms from a documentary language.» back-of-book indexing = creación de los índices de un libro.
Example: This article outlines some of the problems which confronted students attempting to master the skills of back-of-book indexing.» back-of-the-book indexing = creación de los índices de un libro. [Proceso de confección de los índices que aparecen al final de un libro]
Example: Though statistical techniques have a lot to offer for free-text data base systems, neither method has had much success with back-of-the-book indexing.» canonical indexing = indización canónica.
Example: A canonical indexing of molecular graphs based on the maximal digital code corresponding to the lower triangle part of the adjacency matrix is suggested.» catchword indexing = indización por palabras clave del título. [Indización de títulos en la que éstos aparecen debajo de cada una de las palabras claves contenidas en ellos; más conocido como indización al estilo KWOC]
Example: One particular development of catchword indexing is now widely used to produce title indexes on computers.» catchword title indexing = indización por palabras clave del título. [Indización de títulos en la que éstos aparecen debajo de cada una de las palabras claves contenidas en ellos; más conocido como indización al estilo KWOC]
Example: Catchword title indexing has been used for many years in such bibliographical tools as British Books in Print and in the indexes issued by periodicals.» chain indexing = indización en cadena. [Creación de entradas en un índice a partir de los números de clasificación de los documentos]
Example: Chain indexing is so-called because, by this method, the lead term in each alphabetical index entry for a given subject is systematically chosen from the chain of concepts present in the class assigned to that subject.» computer-based indexing system = sistema automatizado de indización.
Example: Since the introduction of computer-based indexing systems alphabetical indexing languages have become more prevalent, and UDC has suffered a reduction in use.» computer indexing = indización automatizada.
Example: In computer indexing this will involve statistical analysis of the relative frequency of occurrence of terms.» controlled indexing language = lenguaje de indización controlado. [Léxico construido o controlado con la ayuda de un conjunto de reglas, que puede unívoca y limitadamente representar el contenido de documentos y demandas]
Example: Controlled indexing languages are indexing languages in which both the terms that are used to represent subjects, and the process whereby terms are assigned to a particular document are controlled or executed by a person.» controlled indexing term = término de indización controlado.
Example: Such systems, then, whilst they can search on controlled indexing terms, are specifically geared towards searching of natural-language terms.» controlled indexing vocabulary = vocabulario de indización controlado.
Example: 'Greenhouses' is not a term in the controlled indexing vocabulary used in the database.» controlled-language indexing = indización en lenguaje controlado.
Example: Controlled-language indexing is extremely time-consuming and costly.» coordinate indexing = indización coordinada.
Example: In searching, we have to have some method of combining concepts, or coordinating them, so that we can perform the required matching operation, and this second method is often known as coordinate indexing.» cycled indexing = indización cíclica.
Example: Cycled indexing involves the movement of the first lead term to the last position in the subsequent entry.» cyclic indexing = indización por ciclos.
Example: Cycled or cyclic indexing is a technique for the movement of the components of index headings in order to generate additional entries.» Deep Structure Indexing System (DSIS) = Sistema de Indización de Estructura Profunda (DSIS).
Example: Deep Structure Indexing System (DSIS) is a version of POPSI (Postulate-based Permuted Subject Indexing).» depth indexing = indización en profundidad, indización exhaustiva. [Proceso de indización por el cual se extrae el máximo número de conceptos contenidos en un documento para su representación en el índice]
Example: Depth indexing aims to extract all the main concepts dealt with in a document for indexing purposes.» depth of indexing = exhaustividad en la indización. [Grado de representación de una materia en el proceso de indización]
Example: The depth of indexing is the degree to which a subject is represented in detail in an indexing process.» derivative indexing = indización derivada automáticamente de los documentos. [Indización obtenida de la manipulación automática de las palabras significativas de los documentos, especialmente los títulos]
Example: A number of writers have pointed out that derivative indexing or the automatic manipulation of title words offers an economical way to index documents at the expense of increased effort during the search stage.» derived indexing = indización derivada automáticamente de los documentos. [Indización obtenida de la manipulación de las palabras significativas de los documentos, especialmente los títulos]
Example: Derived indexing involves the minimum of intellectual effort and is therefore well suited to computer processing.» descriptor indexing = indización por descriptores.
Example: First, a large number of databases that use descriptor indexing still avoid instructions for free-text retrieval.» DISI (Deep Structure Indexing System) = DSIS (Sistema de Indización de Estructura Profunda).
Example: The most recent version of computerised POPSI is known as Deep Structure Indexing System (DSIS).» entity-oriented indexing = indización según el objeto. [En lenguajes documentales, indización que consiste en asignar encabezamientos a los documentos que mejor describan su contenido]
Example: Hutchins' and Moron's concepts of aboutness are described and compared to Soergel's ideas of request-oriented and entity-oriented indexing.» free indexing language = lenguaje de indización libre.
Example: Free indexing language again, is not a listed language of terms which is distinct from the terms used to describe concepts in a subject area.» free language indexing = indización en lenguaje libre.
Example: Free language indexing is distinct from natural language indexing in that natural indexing is constrained by the language of the document being indexed; free language indexing does not even recognise these constraints.» human indexing = indización humana.
Example: It will also be necessary for humans to add call number and subject indexing, although a considerable amount of work has already been done on mechanized subject classification and subject indexing, which is at least as good as human indexing.» indexing agency = agencia de indización.
Example: In-house authority list record the headings that have been established in the past by that indexing agency.» indexing and abstracting service = servicio de indización y resumen.
Example: In such a world, the 'journal' would no longer exist and libraries would be cataloguing at the level of what S.R. Ranganathan called 'micro-thought' -- a level that we have always left to indexing and abstracting services = En este tipo de mundo, la "revista" ya no existiría y las bibliotecas catalogarían al nivel de lo que S.R. Ranganathan denominó "el micropensamiento", un nivel que siempre hemos dejado a los servicios de indización y resumen.» indexing bulletin = boletín de índices. [Publicación que periódicamente indiza los documentos aparecidos sobre una disciplina concreta y que a diferencia de la boletín de resúmenes abstracting bulletin no incluye resúmenes o abstracts]
Example: This information centre produces an indexing bulletin on the role of women, of which half of the subscriptions are from individuals, and half from libraries.» indexing field = campo indizable.
Example: This article discusses the limitations implicit in the indexing of chemical information suggesting that the principal solution for these problems is to load this class of information into separate, chemical, indexing fields.» indexing journal = revista de índices. [Publicación que periódicamente indiza los documentos aparecidos sobre una disciplina concreta y que a diferencia de la revista de resúmenes abstracting journal no incluye resúmenes o abstracts]
Example: Indexing journals (and the indexes to printed abstracting journals) are alphabetical indexes to the literature of a subject area.» indexing language = lenguaje documental, lenguaje de indización. [Lenguaje formalizado usado para describir y representar información o el contenido de los documentos para su almacenamiento y recuperación]
Example: An indexing language is simply defined as a list of terms or notation that might be used as access points in an index or as the set of terms (the vocabulary) and the devices for handling the relationships between them in a system for providing index descriptions.» indexing periodical = revista de indización.
Example: Abstracting and indexing periodicals may be interfiled into a common sequence with other serials, or may form a separate sequence.» indexing phrase = frase de indización. [En indización, frase que describe el contenido del documento a modo de título]
Example: A rule-governed derivation of an indexing phrase from the text of a document is, in Wittgenstein's sense, a practice, rather than a mental operation explained by reference to internally represented and tacitly known rules.» indexing process = proceso de indización.
Example: The indexing process creates a description of a document or information, usually in some recognized and accepted style of format.» indexing service = servicio de indización. [Publicación periódica que contiene índices de los documentos publicados sobre un tema o grupo de temas de especialidad]
Example: The H W Wilson Company of New York is the best known and most prolific publisher of indexing services in specific subject fields.» indexing string = cadena de indización.
Example: All index entries and references in a PRECIS index are derived from an indexing string.» indexing system = sistema de indización.
Example: An indexing system is a set of prescribed procedures for organising the contents of records of knowledge or documents for the purposes of retrieval and dissemination.» indexing term = término de indización. [Representación de un concepto por medio de un término derivado del lenguaje natural o de una notación]
Example: Keywords or indexing terms may serve as a crude indicator of subject scope of a document.» indexing tool = herramienta de indización.
Example: These comments are also intended to demonstrate the similarity between indexing and searching and to show how indexing tools feature in the searching process.» keyword indexing = indización por palabras clave.
Example: Co-word analysis of keywords and titles was undertaken and results suggest that keyword indexing does not distort co-word findings = Se realizó un análisis de coocurrencia de las palabras clave y de los títulos y los resultados indican que la indización por palabras clave no distorsiona los hallazgos de la coocurrencia de palabras.» machine indexing = indización mecanizada.
Example: With machine indexing some irrelevant and redundant entries are inevitable.» manual indexing = indización manual.
Example: The more important physical forms for the future are those which can most effectively be produced from computerised cataloguing systems; however manual cataloguing and indexing are still performed.» natural indexing language = lenguaje de indización natural. [Léxico en lenguaje natural, entresacado del documento y no manipulado por el documentalista]
Example: Natural indexing languages are not really a separate language at all, but the 'natural language' or ordinary language of the document being indexed.» natural language indexing = indización en lenguaje natural.
Example: Natural language indexing has its own solutions for the problems identified below.» Nested Phrase Indexing System (NEPHIS) = Sistema de Indización por Frases Anidadas (NEPHIS).
Example: The package also uses Craven's Nested Phrase Indexing System (NEPHIS), and students can compare the effects of the two methods on the index entries they create.» periodical indexing = vaciado de revistas.
Example: Over the past 10 years, periodicals indexing has greatly changed in terms of production, formats and products, coverage, and producers and users.» periodicals indexing service = servicio de indización de publicaciones periódicas. [Publicación periódica que contiene índices de los artículos publicados en las publicaciones periódicas especializadas]
Example: From the point of view of bibliographic control, periodicals indexing services have the advantage of currency, for most of them are published at least quarterly.» permuted title indexing = indización permutada de títulos.
Example: Permuted title indexing selects keywords from the title to be used as subject headings.» post-coordinated indexing = indización postcoordinada. [Indización de documentos sin la ayuda de un order de encabezamientos o de notaciones establecido previamente]
Example: The indexing of documents without a pre-established order of terms of class marks is known as post-coordinated indexing.» post-coordinate indexing system = sistema de indización postcoordinada. [Sistema que combina los diferentes conceptos (por tanto términos de indización) que conforman una materia en el momento de la búsqueda]
Example: Post-coordinate indexing systems start from the same identification of multi-concept subjects and their component unit concepts as pre-co-ordinate indexing systems.» Postulate-based Permuted Subject Indexing (POPSI) = Indización Permutada de Materias basada en Postulados (POPSI).
Example: Postulate-based Permuted Subject Indexing (POPSI) is an innovative verbal classification system based primarily on Ranganathan's postulates redefined in a lucid way by Bhattacharyya.» PRECIS indexing = indización PRECIS.
Example: PRECIS indexing, cycled indexing, rotated indexing and SLIC indexing are all different types of shunted indexes in which the components of index headings are moved to generate additional entries.» PRECIS indexing system = sistema de indización PRECIS.
Example: The PRECIS indexing system (Preserved Context Indexing System) is a set of procedures for producing index entries.» pre-coordinated indexing = indización precoordinada. [Indización de documentos por la que el orden de los encabezamientos o las notaciones se establecen de acuerdo con un sistema de indización]
Example: The indexing of documents where the order of terms or class marks is established according to a documentary language or indexing system is known as pre-coordinated indexing.» pre-coordinate indexing system = sistema de indización precoordinada. [Sistema que combina los diferentes conceptos (por tanto términos de indización) que conforman una materia en el momento de la indización, o sea antes del almacenamiento]
Example: Pre-co-ordinate indexing is conventional indexing of the type commonly found in printed indexes, where a document is represented in the index by a heading or headings consisting of a chain of terms.» probabilistic indexing = ?.
Example: The concept of ranking of the output to a search is an important one, and is one of the objectives of approaches such as the use of fuzzy sets or probabilistic indexing.» request-oriented indexing = indización según la demanda. [En lenguajes documentales, indización que consiste en asignar encabezamientos a los documentos que respondan a la terminología usada por los usuarios para recuperarlos]
Example: Hutchins' and Moron's concepts of aboutness are described and compared to Soergel's ideas of request-oriented and entity-oriented indexing.» rotated indexing = indización por rotación.
Example: Rotated indexing involves each element in turn becoming the heading under which an entry is filed, but no change in citation order takes place.» SLIC indexing = indización SLIC.
Example: SLIC indexing or Selective Listing in Combination involves the combination of elements, but in one direction only.» subject indexing = indización por materias, asignación de materias.
Example: A fundamental theoretical rule of subject indexing is that each heading should be co-extensive with the subject of the document, that is, the label and the information or documents found under that label should match.» systematic indexing = indización sistemática.
Example: In 1911 J Kaiser published a work entitled 'Systematic Indexing,' which took the practice of alphabetical subject indexing an important step forward.» title-term indexing = indización por palabras del título.
Example: It has been said that Cutter in developing his method of alphabetic subject indexing 'dealt the death blow' to ninenteenth-century title-term indexing.